Geminids Meteor Shower 2024: A Spectacular Celestial Display You Won’t Want to Miss
Hey there, stargazers! December is often associated with cozy nights by the fire, holiday cheer, and… a breathtaking celestial spectacle: the Geminids meteor shower. If you’re even remotely curious about the night sky, mark your calendars for December 2024 because this year’s Geminids promise to be something truly special. This isn’t just another meteor shower; it’s a dazzling display of shooting stars that’ll leave you speechless. Let’s dive into everything you need to know to make the most of this incredible astronomical event.
What are the Geminids, and Why Are They So Special?
Unlike most meteor showers that originate from comets, the Geminids are unique. Their source is an unusual object called 3200 Phaethon, which is classified as either a rock comet or a Pallas-type asteroid. This makes the Geminids a bit of a cosmic mystery, adding to their allure. Phaethon leaves behind a trail of dusty debris as it orbits the sun, and every year in December, Earth passes through this debris field. As these tiny particles burn up in our atmosphere, we witness the spectacular streaks of light we call meteors.
What sets the Geminids apart from other showers, like the Perseids in August, is their sheer abundance. Under ideal conditions, you can witness upwards of 120 meteors per hour at their peak! That’s a meteor almost every 30 seconds – a truly incredible sight. And the Geminids are known for their bright, colorful streaks, often leaving persistent trails that linger for a few seconds after the initial flash. I remember witnessing the Geminids a few years ago, and the sheer number and brilliance of the meteors left me completely awestruck. It felt like the sky was raining stars!
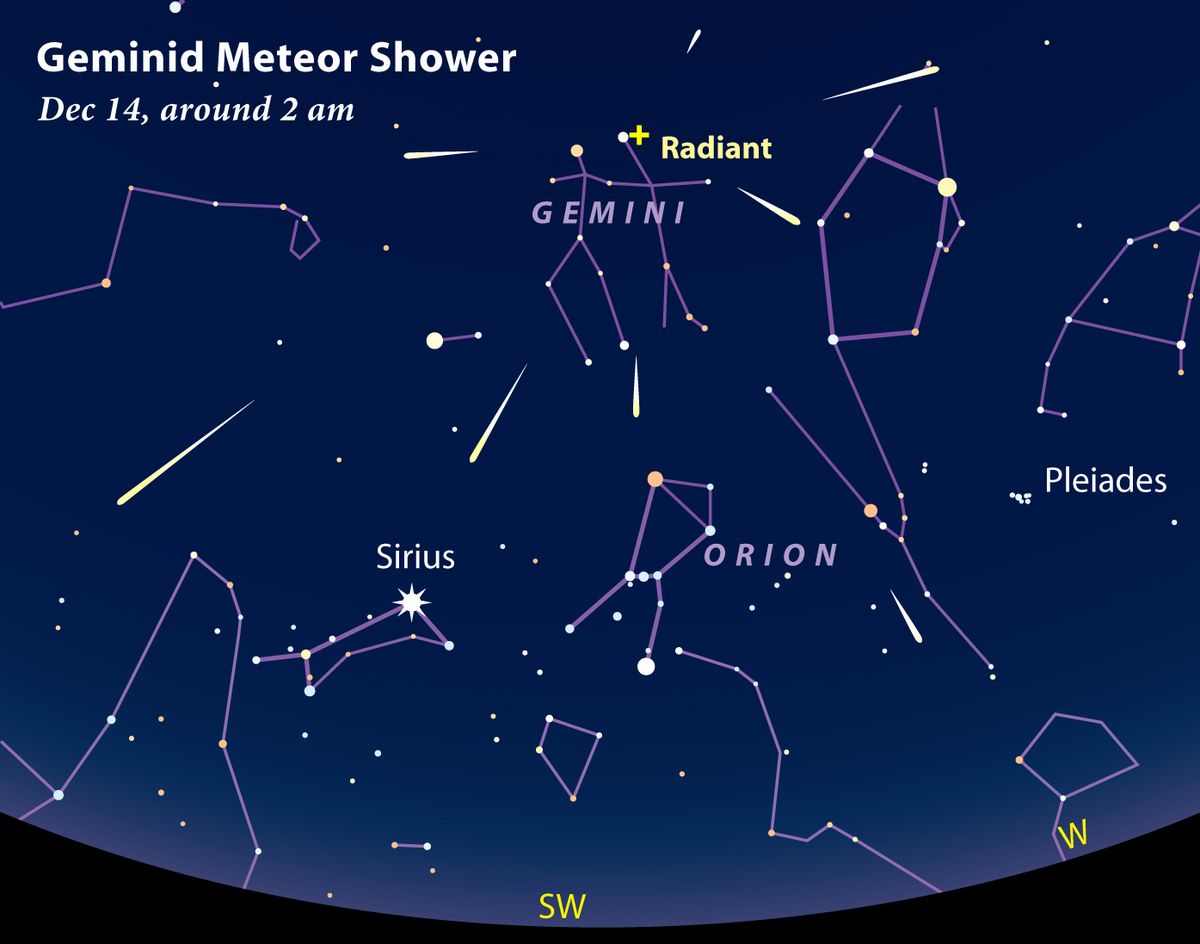
When and Where to See the Geminids in 2024

Timing is everything when it comes to meteor showers. For the Geminids in 2024, the peak activity is expected to fall around December 13-14. However, you’ll likely see a good show a night or two before and after the peak as well. The best time to watch is typically after midnight, when the radiant point (the point in the sky from which the meteors appear to originate) is high in the sky.
The radiant point for the Geminids is in the constellation Gemini, hence the name. To find Gemini, look for the bright stars Castor and Pollux. However, you don’t need to pinpoint Gemini precisely; the meteors will appear all across the sky.
Here’s a handy checklist for optimal viewing:
- Find a dark location: Light pollution is the enemy of meteor watching. Get away from city lights, ideally to a rural area with minimal light interference. National parks or dark sky reserves are excellent choices.
- Give your eyes time to adjust: It takes about 20-30 minutes for your eyes to fully adapt to the darkness. Avoid looking at your phone or other bright lights during this time.
- Bring a blanket or chair: You’ll be spending some time lying down or sitting, so comfort is key.
- Dress warmly: December nights can be chilly, especially if you’re in a location away from city lights.
- Be patient: Meteor showers are a waiting game. Relax, enjoy the night sky, and let the show unfold.


Beyond the Basics: Understanding Meteor Showers
Let’s delve a little deeper into the science behind these spectacular events. A meteor, often called a "shooting star," is the visible path of a meteoroid as it enters the Earth’s atmosphere. This meteoroid is a small piece of rock or dust, often left behind by a comet or, in the case of the Geminids, an asteroid.
As the meteoroid hurtles through the atmosphere at incredible speeds, it collides with air molecules. This friction generates intense heat, causing the meteoroid to vaporize and produce a bright streak of light. The size and composition of the meteoroid determine the brightness and duration of the meteor. Larger meteoroids can produce spectacular fireballs, while smaller ones might only create fleeting streaks.
The Geminids are particularly notable for their relatively slow speed compared to other meteor showers. This slower speed allows for more prolonged viewing of the streaks, making them even more captivating.
Mythology and Folklore Surrounding Meteor Showers

Throughout history, cultures around the world have interpreted meteor showers in various ways, often weaving them into their myths and legends. Some cultures viewed them as omens, while others saw them as celestial blessings or messages from the gods. For example, some Native American tribes associated meteor showers with the spirits of their ancestors returning to Earth. These interpretations highlight the deep connection humans have always had with the cosmos and the wonder they inspire.
The Geminids, with their vibrant display, have undoubtedly inspired countless stories and beliefs over the centuries. While we now have a scientific understanding of their origin, the magical feeling of watching these shooting stars remains a powerful and awe-inspiring experience.
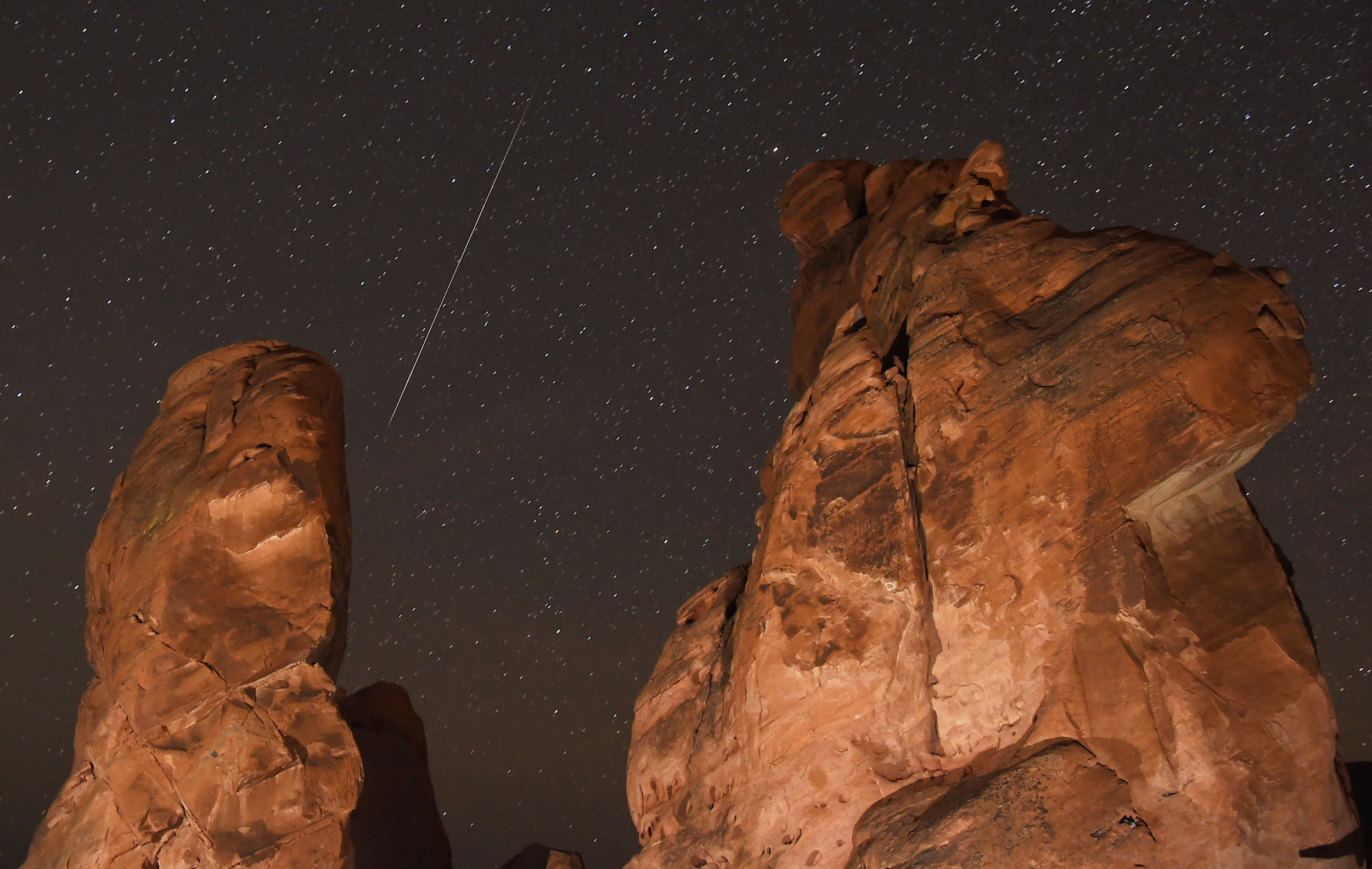
Photography and Astrophotography of the Geminids
Capturing the beauty of the Geminids on camera can be a rewarding challenge. While capturing a single meteor might require some luck, with a bit of preparation, you can increase your chances of success.